accumulated earnings tax irs
What is the Accumulated Earnings Tax. Deductions are allowed for federal income taxes paid excess profit taxes paid to foreign.

Cares Act Implications On Corporate Earnings And Profits E P
535 a Accumulated taxable income means the taxable income of the corporation MINUS ALL of the following.

. The IRS also allows certain exemptions based on the required need for the accumulated earnings. There is a certain level in which the number of earnings of C corporations can get. Accumulated Earnings Tax.
It compensates for taxes which cannot be levied on dividends. IRC 532 a states that the accumulated earnings tax imposed by IRC 531 shall apply to every corporation other than those described in subsection IRC 532b formed or availed of for the purpose of avoiding the income tax with respect to its shareholders or the shareholders of any other corporation by permitting earnings and profits to accumulate instead of being. The AET is a penalty tax imposed on corporations for unreasonably accumulating earnings.
Accumulated Earnings Tax Details. EP as it is widely referred to is an accounting term used to refer to the shareholders of companies. Understanding Accumulated Earnings Profits EP Taxes.
As a practical matter the tax is col-. ACCUMULATED TAXABLE INCOME. Internal Revenue Service IRS sets the accumulated earnings tax scheme to prevent companies from excessively accumulating their income and to pay dividends instead.
The tax rate on accumulated earnings is 20 the maximum rate at which they would be taxed if distributed. A corporation determines this amount by adjusting its taxable income for economic items to better reflect how much cash it has available to make dividend distributions. The accumulated earnings tax rate is 20.
The tax rate on accumulated earnings is 20 the maximum rate at which they would be taxed if distributed. Breaking Down Accumulated Earnings Tax. 10716 substituted equal to the product of the highest rate of tax under section.
However if a corporation allows earnings to accumulate beyond the reasonable needs of the business it may be subject to. The Accumulated Earnings Tax is computed by multiplying the Accumulated Taxable Income IRC Section 535 by 20. The AET is a 20 annual tax imposed on the accumulated taxable income of corporations.
Accumulated earnings and profits EP are the earnings accumulated by a company after the payment of dividends to shareholders. Pursuant to 26 USC. 112240 substituted 20 percent for 15 percent.
A corporation can accumulate its earnings for a possible expansion or other bona fide business reasons. He accumulated earnings tax AET is imposed by Internal Revenue Code IRC section 531 on C corporations formed or availed of for the purpose of avoiding the imposi-tion of income tax on their shareholders by permitting earnings and profits to be accumulated instead of being distrib-uted. Accumulated Earnings Tax The AET is a 20 percent tax for each tax year on accumulated taxable income of corporations1 While the AET hasnt been widely imposed or litigated in recent years it still applies to all corporations with limited exceptions2.
The Accumulated Earnings Tax is more like a penalty since it is assessed by the IRS often years after the income tax return was filed. Exemption levels in the amounts of 250000 and 150000 depending on the company exist. The base for the accumulated earnings penalty is accumulated taxable income.
531-537 and the personal holding company PHC tax under Secs. The accumulated earnings tax also called the accumulated profits tax is a tax on abnormally high levels of earnings retained by a company. If a C corporation retains earnings doesnt distribute them to shareholders above a certain amount an amount which the IRS concludes is beyond the reasonable needs of the business the corporation may be assessed tax penalty called the accumulated earnings tax IRC section 531 equal to 20 percent 15 prior to 2013 of.
The tax rate on accumulated taxable income currently stands at 20 and fortunately the American Taxpayer Relief Act ATRA kept it from rising to a. 10827 substituted equal to 15 percent of the accumulated taxable income for equal to the product of the highest rate of tax under section 1c and the accumulated taxable income. If the accumulated earnings tax applies interest applies to the tax from the date the corporate return was originally due without extensions.
Publicly held corporations with many. The AET is a penalty tax imposed on corporations for unreasonably accumulating earnings. It applies to all corporations unless an exception applies that are formed or availed of for the purpose of avoiding the income tax by.
The threshold is 25000 without accumulated earning tax. However if a corporation allows earnings to accumulate beyond the reasonable needs of the business it may be subject to an accumulated earnings tax of 396. IRC Section 535c1 provides that.
Accumulated Earnings Tax can be reduced by reducing Accumulated Taxable Income. To determine if the corporation is subject to this tax first treat an. These are the accumulated earnings tax AET under Secs.
Dividends Paid In That. If a corporation pursues an earnings accumulation strategy where the accumulation is to avoid the tax on dividends rather than having a business purpose then IRC 532 provides an accumulated earnings tax that can be assessed on accumulated earnings with no clear business purpose. It measures a companys ability to pay cash distributions.
The tax is in addition to the regular corporate income tax and is assessed by the IRS typically during an IRS audit. This tax evolved as shareholders began electing to have companies retain earnings rather than pay them out as dividends in an effort to avoid. According to the IRS anything.
The accumulated earnings tax imposed by section 531 shall apply to every corporation other than those described in subsection b formed or availed of for the purpose of avoiding the income tax with respect to its shareholders or the shareholders of any other corporation by permitting earnings and profits to accumulate instead of being divided or distributed. The tax is in addition to the regular corporate income tax and is assessed by the IRS typically during an IRS audit. When the revenues or profits are above this level the firm will be subjected to accumulated earnings tax if they do not distribute the dividends to shareholders.

Earnings And Profits Computation Case Study
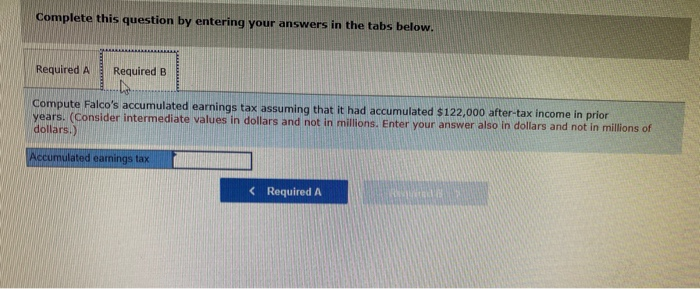
Solved During A Recent Irs Audit The Revenue Agent Decided Chegg Com
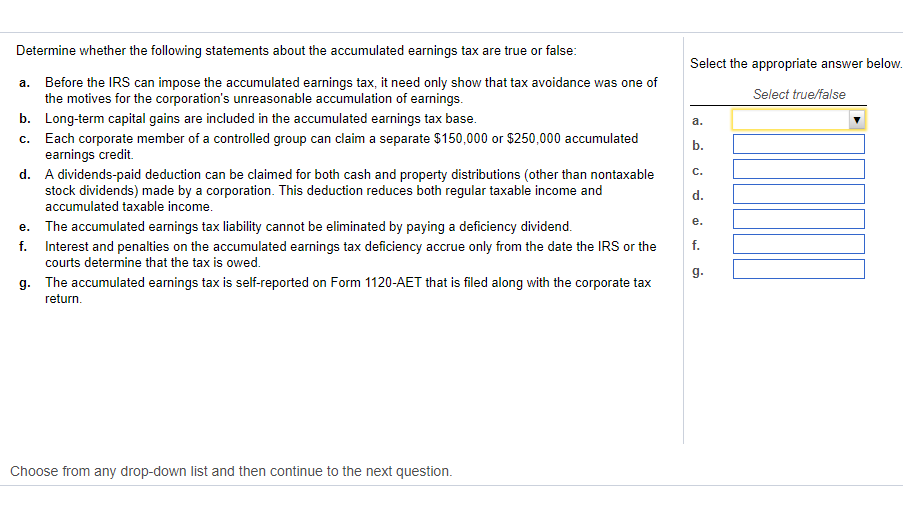
Solved Determine Whether The Following Statements About The Chegg Com

Irs Use Of Accumulated Earnings Tax May Increase
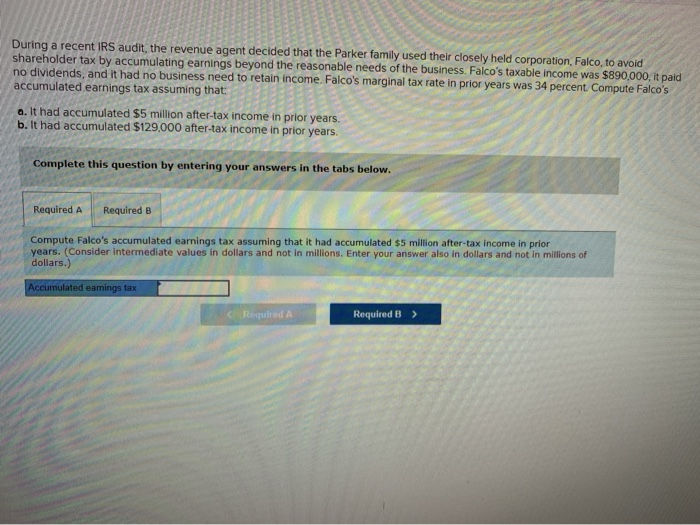
Solved During A Recent Irs Audit The Revenue Agent Decided Chegg Com

Corporate Tax Copyright Ppt Download

Reg 2 Corporate Taxation Flashcards Quizlet

Strategies For Avoiding The Accumulated Earnings Tax Krd

Understanding The Accumulated Earnings Tax Before Switching To A C Corporation In 2019

Earnings And Profits Computation Case Study

How To Calculate The Accumulated Earnings Tax For Corporations Universal Cpa Review

How Corporations May Run Afoul Of The Accumulated Earnings Tax A Section 1202 Planning Brief Frost Brown Todd Full Service Law Firm
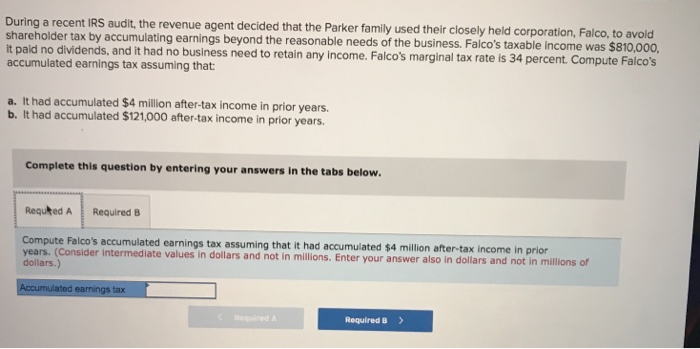
Solved During A Recent Irs Audit The Revenue Agent Decided Chegg Com
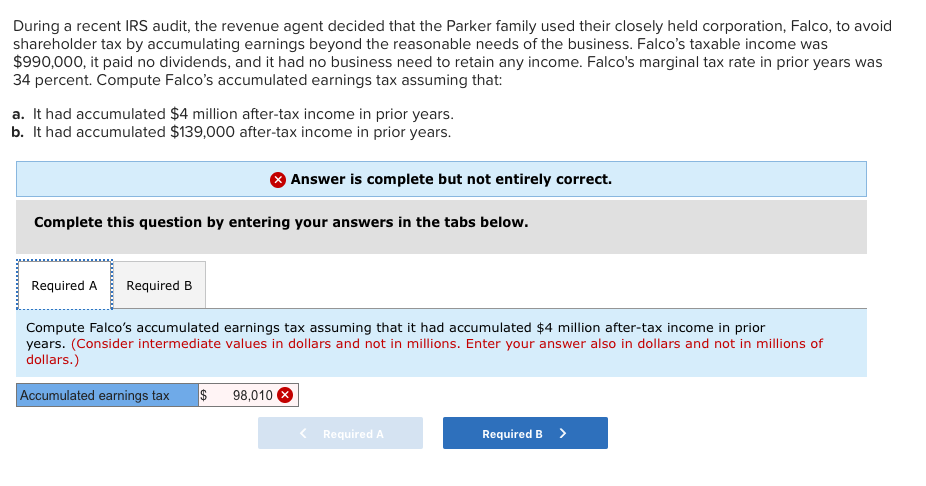
Solved During A Recent Irs Audit The Revenue Agent Decided Chegg Com

Bardahl Formula Calculator Defend Against Accumulated Earnings Tax

Determine Whether The Following Statements About The Accumulated Eangstax Are True Or False A Before The Homeworklib